Introduction to Cold Room Cooling Systems
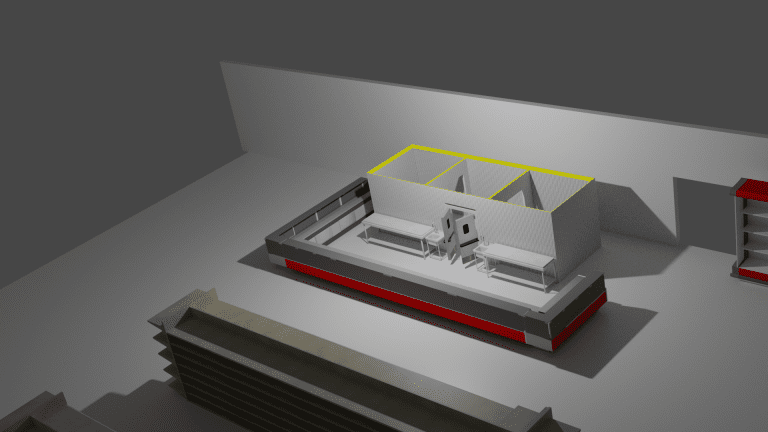
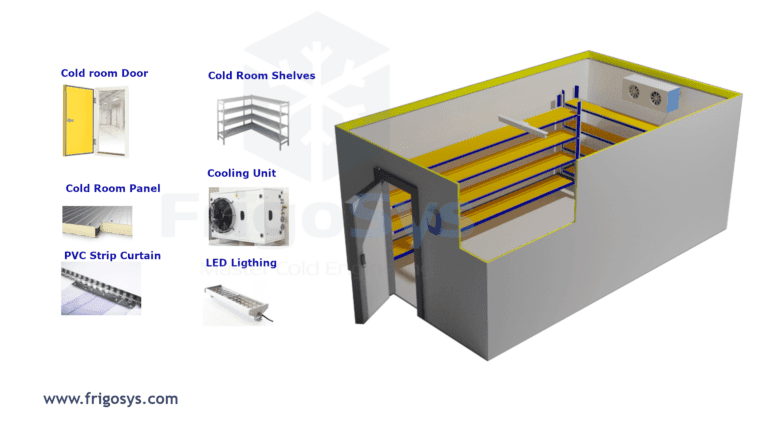
Cold room cooling systems are essential in maintaining low temperatures to store perishable goods, pharmaceuticals, and other temperature-sensitive products. These systems ensure a stable environment, preventing spoilage and extending shelf life.
Key Components
- Cooling Units: Comprised of split cooling units and central cooling units.
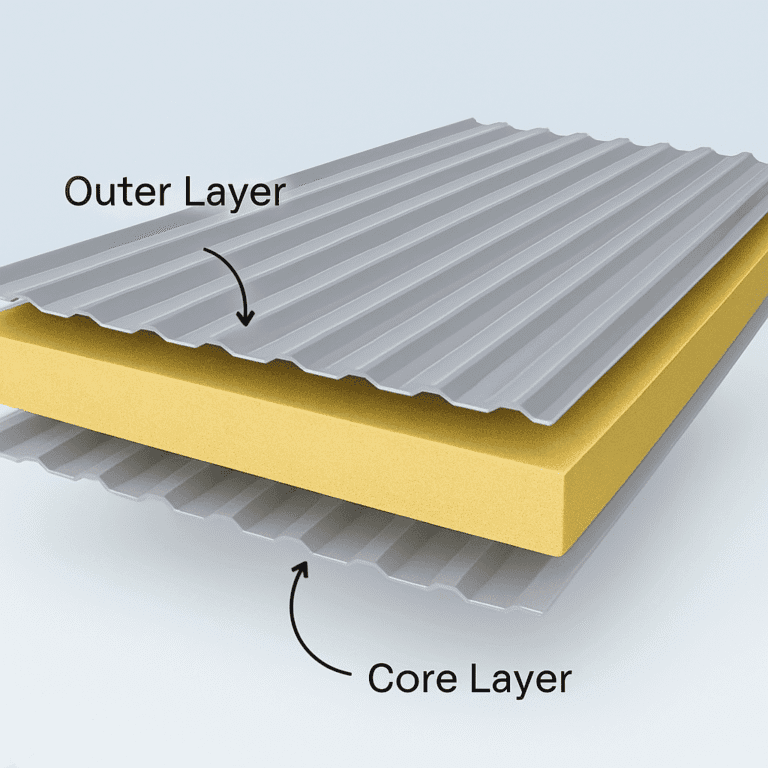
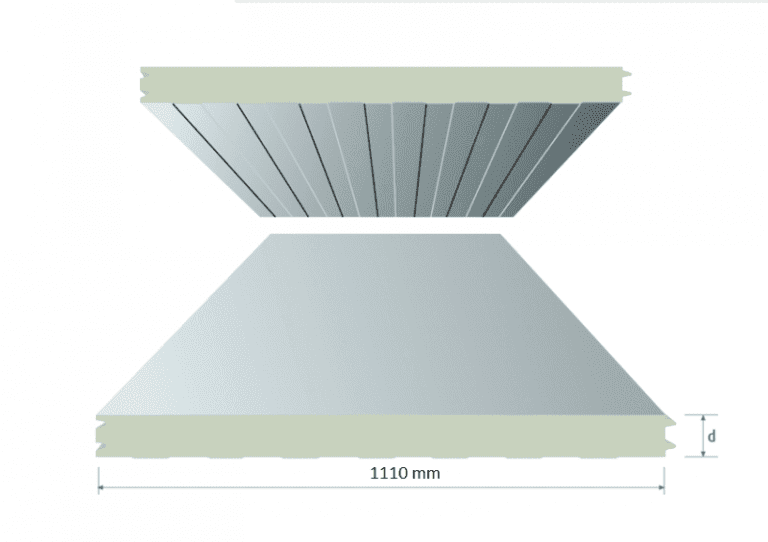
- Insulation: High-quality insulation to minimize thermal exchange.
- Control Systems: Automated controls to manage temperature and humidity.
Benefits of Cold room cooling systems
- Preservation: Keeps products fresh and safe.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimised designs to reduce energy consumption.
- Reliability: Built to maintain consistent performance.
Understanding Market Type Coolers
Market-type coolers are specifically designed for commercial and industrial applications where large quantities of goods need to be stored at consistent and controlled temperatures. These coolers are often used in:
- Supermarkets
- Food processing plants
- Warehouses
Key features of market-type coolers include:
- High Capacity: Capable of handling substantial volumes of goods.
- Energy Efficiency: Often designed to minimise energy consumption.
- Ease of Maintenance: Built to allow easy access for repairs and refrigerant recharge.
- Climate Control: Provides precise temperature control to maintain product quality.
Experts often recommend these coolers for environments needing reliable and durable cooling solutions.
The Importance of Proper Cooling for Market Coolers
Proper cooling in market coolers is vital for numerous reasons. It ensures the longevity and freshness of perishable goods such as fruits, vegetables, dairy, and meats. Effective cooling prevents spoilage, which reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses.
- Maintaining Product Quality: Temperature consistency prevents degradation of taste and texture.
- Safety: Proper cooling minimizes bacterial growth, which ensures consumer safety.
- Energy Efficiency: Efficient cooling systems reduce energy consumption, lowering operational costs.
- Compliance: Market coolers must meet regulatory requirements for food storage, with proper cooling being central to compliance.
Ensuring proper cooling is essential for maintaining product integrity, safety, and operational efficiency.
Key Features to Look for in a Cold Room Cooling Systems
When selecting a cooling system for cold rooms, it is vital to evaluate certain features that ensure efficiency and reliability.
- Energy Efficiency: Prioritise systems with high energy ratings to reduce operational costs.
- Temperature Range: Ensure the unit can maintain the required temperature range specific to storage needs.
- Cooling Capacity: Confirm the system’s capacity matches the square footage and thermal load of the cold room.
- Maintenance Requirements: Opt for systems with easy maintenance and readily available replacement parts.
- Noise Levels: Consider the unit’s noise output, especially if the cold room is near occupied areas.
- Control Features: Look for advanced control options, such as digital thermostats and remote monitoring.
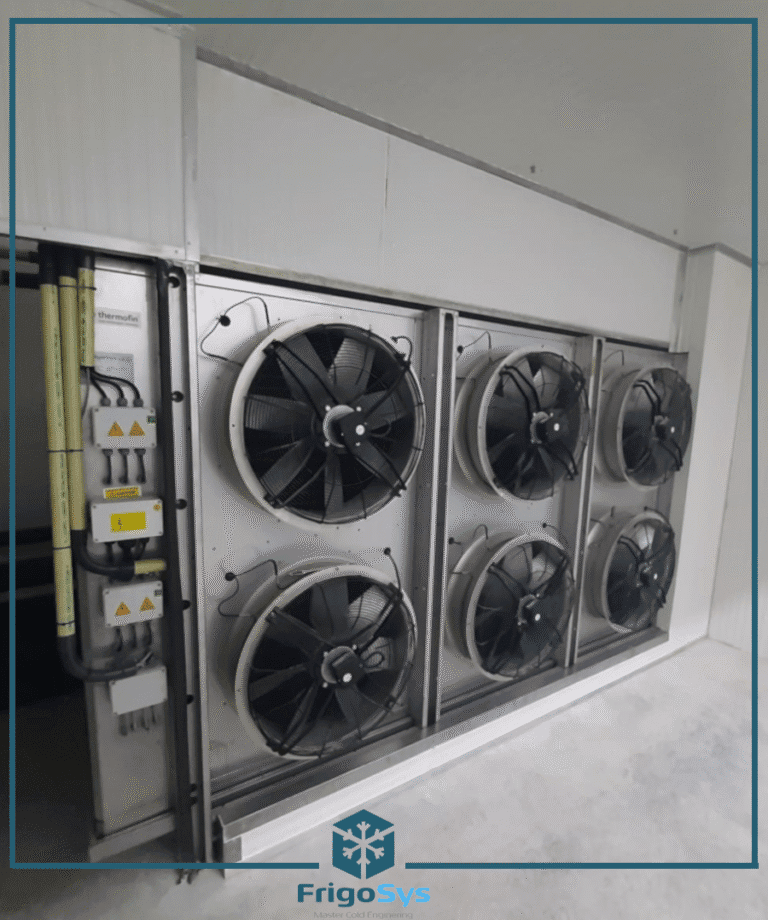
Types of Cold Room Cooling Systems
Cold rooms utilize different types of cooling systems to maintain low temperatures and ensure the preservation of perishable goods.
- Split Cooling Units: These systems consist of an evaporator inside the cold room and a condenser unit outside. They are widely used for small to medium-sized cold rooms due to their energy efficiency and ease of installation.
- Central Cooling Units: These systems feature a central refrigeration plant that serves multiple cold rooms or zones. They are ideal for large facilities as they offer higher efficiency for bulk cooling needs.
- Air-Cooled Systems: Utilise fans to disperse cool air. They are suitable for environments where water availability is limited.
- Water-Cooled Systems: These use water to absorb heat and are appropriate for settings that have reliable water sources and need more efficient cooling.
Overall, the choice depends on specific requirements like the size of the cold room, energy efficiency, and the available infrastructure.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Considerations for Cold room cooling systems
Energy efficiency and cost considerations are critical when comparing split cooling units and central Cold room cooling systems.
Energy Efficiency
- Split Cooling Units:
- Often allow for zoning, leading to potentially lower energy consumption.
- It can be turned off in unused sections, saving energy.
- Generally, they have higher SEER ratings.
- Central Cooling Units:
- Efficient for large, uniform spaces.
- May require more energy if zones are not independently controlled.
- Often maintain constant temperature throughout the facility.
Cost Considerations
- Initial Installation:
- Split units typically cost less to install initially.
- Central units may have higher upfront costs due to ductwork and system design.
- Maintenance:
- Split units are generally easier and cheaper to maintain.
- Central systems may require more specialized service.
Cold room cooling systems Cooling Capacity and System Sizing
Cooling capacity is crucial for cold rooms. The cooling unit must maintain a consistent temperature despite constant door openings or large quantities of fresh goods entering.
- Split Cooling Units:
- Divided into two parts: indoor and outdoor.
- Easier to install in smaller spaces.
- Option to tailor system size to capacity needs.
- Central Cooling Units:
- Single, large unit supporting the entire cold room.
- More suitable for larger areas.
- Requires more intricate installation and space.
Selecting the right system based on room size and required cooling capacity ensures efficient operations and energy use.
Temperature Control and Monitoring
Both split cooling units and central cooling units enable precise temperature control and monitoring, essential for cold rooms’ functionality and efficiency.
Split Cooling Units
- Each unit operates independently, allowing tailored temperature settings for specific areas.
- Easier to monitor and adjust temperatures for small, separate zones.
- Redundancy ensures temperature stability even if one unit fails.
Central Cooling Units
- The centralised control system manages the whole cold room.
- Consistent temperature across larger spaces, is beneficial for uniform storage conditions.
- Advanced monitoring systems detect fluctuations and alert operators, ensuring reliable performance.
These systems offer unique advantages based on the scale and specific requirements of cold room operations.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Split Cooling Units
- Ease of Installation: These units typically require less structural modification.
- Space Efficiency: The indoor and outdoor units can be placed strategically.
- Cost: Initial installation may be cheaper due to minimal ductwork.
- Maintenance:
- Requires routine checks of both indoor and outdoor units.
- Filter replacements are necessary periodically.
- Professional servicing annually to ensure peak performance.
Central Cooling Units
- Installation Complexity: Requires extensive ductwork and may involve structural changes.
- Space Requirement: Needs more space for duct networks.
- Cost: Installation can be more expensive due to higher complexity.
- Maintenance:
- Regular inspection and cleaning of ducts.
- Periodic coolant level checks.
- Annual professional maintenance to handle system intricacies.
Environmental Impacts and Sustainability
Both split cooling units and central cooling units have distinct environmental and sustainability profiles.
Split Cooling Units
- Increased energy efficiency for smaller spaces.
- Potential for reduced refrigerant leaks due to smaller system size.
- May require more units, leading to increased material use and waste.

Central Cooling Units
- More energy-efficient for larger spaces or entire facilities.
- Use larger amounts of refrigerants, with a higher potential for leaks.
- Generally, longer-lasting with proper maintenance, reducing waste.
Continuous technological advancements aim to improve the sustainability of both types.

Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them Cold room cooling systems
1. Initial Cost:
- Split Units: Higher due to multiple units and installations.
- Central Units: Expenses concentrated in a single system.
Solution: Budget planning and phased installations can help manage costs.
2. Maintenance Complexity:
- Split Units: Individual units increase maintenance points.
- Central Units: Centralised, easier to manage but one failure can disrupt entire cooling.
Solution: Regular, scheduled maintenance and having spare parts on hand.
3. Energy Efficiency:
- Split Units: Can be less efficient if not optimally used.
- Central Units: Generally more efficient but require proper management.
Solution: Invest in energy-efficient models and regular energy audits.
Case Studies and Real-world Applications
Warehouse Application
A food distribution center implemented a central cooling unit to manage temperature across various loading bays. This central unit ensured a uniform temperature, minimizing the risk of spoilage. Maintenance staff appreciated the centralized control system.
Pharmaceutical Storage
A pharmaceutical company used split cooling units in multiple storage rooms. This enabled precise temperature control for different medications. The split units allowed for quick adjustments and isolated maintenance, ensuring minimal disruption.
Retail Scenario
A supermarket chain compared both systems in different branches. Stores with split units reported lower energy consumption during off-peak hours. Conversely, central units proved more efficient during high-demand periods.
Tips for Choosing the Right Supplier
Selecting the right supplier for cooling units involves several considerations:
- Reputation: Investigate the supplier’s reputation within the industry.
- Experience: Choose suppliers with extensive experience in supplying cooling units.
- Product Quality: Ensure their products meet industry standards for reliability and performance.
- Customer Support: Evaluate their customer service and after-sales support.
- Price: Compare prices and ensure they offer value for money.
- Delivery Times: Assess their ability to deliver on time.
- Warranty: Check the warranty terms they provide.
These factors help in finding a reliable supplier that aligns with the specific needs for Cold room cooling systems
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision
Choosing between split Cold room cooling systems and central cooling units for cold rooms requires careful consideration of various factors.
- Budget Constraints: Split cooling units often entail lower initial investment.
- Energy Efficiency: Central units may offer better long-term energy savings.
- Installation Space: Split units are preferable for smaller spaces or buildings with limited ductwork options.
- Maintenance Needs: Central units are generally easier to service due to their consolidated structure.
Ultimately, the decision depends on the specific requirements of the cold room, including size, usage patterns, and energy goals. Consulting with HVAC professionals can aid in making the best choice.