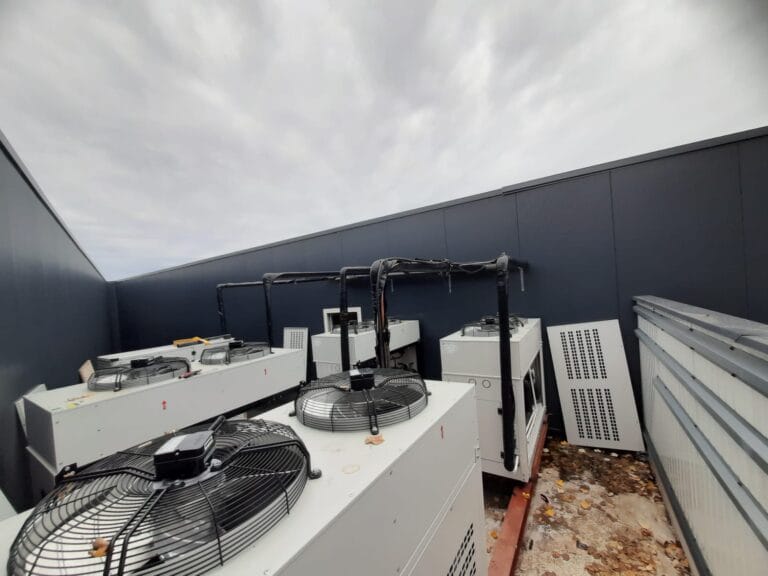
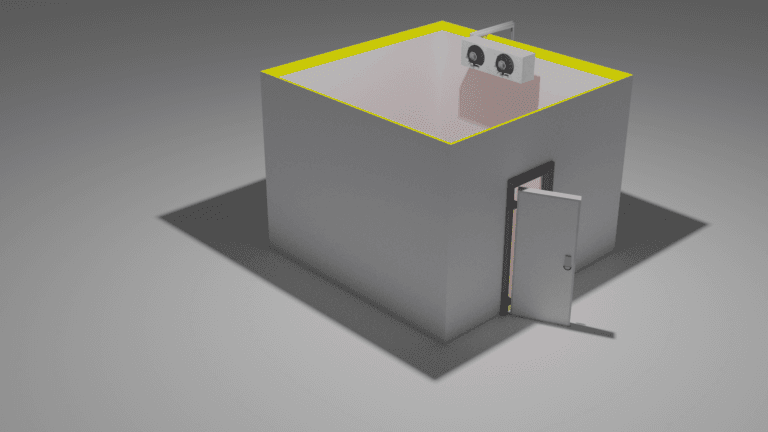
Key features of cold room evaporators include:
- Coils: Comprised of copper or aluminum for efficient thermal conductivity.
- Fans: Circulate air, enhancing heat transfer.
- Defrost Mechanisms: Prevent ice buildup to maintain functionality.
Their performance directly impacts operational efficiency, product preservation, and energy consumption.
The Science Behind Cold Room Evaporators: How They Work
Cold room evaporators are critical components in the refrigeration cycle, facilitating heat exchange to maintain low temperatures. They utilize thermodynamic principles, absorbing heat from the refrigerated space and transferring it to the refrigerant circulating through the evaporator coils. As warm air passes over the coils, the refrigerant inside evaporates, transitioning from a liquid to a gaseous state. This process effectively extracts heat.
Evaporator fans enhance airflow, ensuring even cooling throughout the cold room. Additionally, defrost mechanisms prevent ice buildup on the coils, maintaining efficiency and consistent performance in various operating conditions.
Key Features of Modern Cold Room Evaporators
- Efficient Heat Exchange: Modern cold room evaporators are designed to optimize heat transfer, facilitating rapid cooling and maintaining consistent temperatures within cold storage environments.
- Energy Efficiency: Most systems incorporate energy-saving technologies, such as variable-speed fans, to reduce power consumption while ensuring optimal performance.
- Corrosion Resistance: Advanced materials, including aluminum and stainless steel, are widely used to prevent rust and extend the lifespan of components in humid environments.
- Compact Designs: Sleek and space-saving designs allow for maximum storage capacity without compromising airflow or cooling efficiency.
- Noise Reduction: Enhanced engineering minimizes operational noise, ensuring a quieter environment during usage.
- Defrosting Mechanisms: Built-in automatic defrosting systems prevent ice buildup, ensuring consistent operation and minimizing maintenance needs.
Different Types of Cold Room Evaporators and Their Applications
Cold room evaporators are essential components of refrigeration systems, each type catering to specific operational needs. They can be classified based on design, functionality, and application.
1. Ceiling-Mounted Evaporators
- Ideal for tight spaces with limited floor area.
- Commonly used in commercial cold rooms for frozen food storage.
- Provide even air distribution to maintain uniform temperatures.

Cold room Evaporators
2. Floor-Mounted Evaporators
- Suitable for large cold rooms requiring high cooling capacity.
- Frequently used for industrial applications, such as meat or produce storage.
- Offer easy maintenance and high durability.

3. Wall-Mounted ( Cubic ) Evaporators
- Designed for spaces requiring targeted cooling.
- Commonly found in small, specialized storage environments.
- Effective for cold rooms storing perishable goods like dairy or flowers.
Each type ensures optimized operation depending on the storage requirements and environmental conditions.

Why Cold Room Evaporators Are Essential for Temperature Control
Cold room evaporators are vital in maintaining precise temperature control within refrigeration systems. They ensure the effective transfer of heat by facilitating the conversion of liquid refrigerant into vapor, which absorbs excess heat from the air inside the cold room. This process is critical for preserving perishable goods, maintaining storage quality, and preventing spoilage.
Evaporators also regulate humidity levels, safeguarding items vulnerable to water damage or mold. Advanced evaporator designs reduce energy consumption, enhancing system efficiency. By delivering uniform cooling throughout the space, these units help eliminate hot spots, ensuring optimal conditions for storage and preservation.
Common Problems with Cold Room Evaporators and How to Fix Them
Cold room evaporators can experience several issues that compromise cooling efficiency. Common problems include:
- Ice Build-Up on Coils: Ice formation reduces heat absorption. Regular defrosting and verifying defrost cycle settings can address this. Ensure proper airflow and check for blocked fans.
- Leaking Refrigerant: Low refrigerant levels reduce cooling capacity. Technicians must inspect for leaks, repair them, and recharge the system to the required levels.
- Fan Malfunction: Fan issues disrupt air distribution. Cleaning or replacing faulty motors or blades resolves this.
- Electrical Faults: Loose wires or damaged connections impact evaporator operations. A thorough electrical inspection and replacement of compromised components prevent system failure.
- Insufficient Airflow: Blocked vents or clogging impede performance. Regular maintenance, including cleaning air filters and ensuring unobstructed airflow, optimizes efficiency.
Energy Efficiency and Maintenance of Cold Room Evaporators
Efficient performance of cold room evaporators is crucial for minimizing energy consumption and maintaining optimal storage conditions. Regularly cleaning evaporator coils ensures unobstructed airflow, which prevents the system from overexerting itself. Monitoring refrigerant levels is essential to avoid inefficiencies caused by leakage or undercharging.
Proper defrosting of evaporators prevents excessive frost buildup, which can insulate coils and hinder heat transfer. Implementing energy-efficient fans, or variable-speed motors, reduces electricity usage by optimizing airflow according to cooling demands. Scheduled inspections allow for the early identification of worn-out components or electrical issues.
Operators should also ensure accurate thermostat calibration to prevent overcooling, which needlessly increases energy expenditure.
The Role of Cold Room Evaporators in the Food and Pharmaceutical Industries
Cold room evaporators are pivotal in maintaining optimal storage conditions within the food and pharmaceutical sectors. By regulating temperature and humidity, they prevent the degradation of temperature-sensitive items, ensuring product safety and quality.
In the Food Industry:
- Preservation of Perishables: Cold room evaporators help preserve freshness in fruits, vegetables, dairy, and meat by preventing spoilage and microbial growth.
- Compliance with Regulations: Their use ensures adherence to stringent food safety standards.
In the Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Storage of Medicines: Evaporators reliably maintain strict temperature ranges for vaccines, drugs, and biological samples.
- Minimization of Contamination: They reduce risks associated with fluctuating temperatures, safeguarding product efficacy.
Consistent environmental control underscores their essential role in both industries.
How to Choose the Right Cold Room Evaporators for Your Needs
Selecting the right cold room evaporator requires evaluating several factors to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency. Start by determining the intended application, whether for chilling, freezing, or storing perishable items. Assess the size of the cold room, as larger spaces demand evaporators with higher cooling capacities.
Consider the refrigerant compatibility, ensuring the evaporator matches your refrigeration system. Evaluate the air circulation requirements to prevent hot spots and maintain an even temperature—factor in energy efficiency ratings to reduce operational costs.
Additionally, pay attention to the construction material, prioritizing durability and corrosion resistance for long-term performance in humid conditions.