Introduction to Cold Storage Solutions
In today’s world, the preservation of perishable goods is as crucial as ever. Whether for pharmaceutical products, food items, or technological components, the ability to maintain a consistent and controlled cold environment is vital. Cold storage solutions have thus become an indispensable part of various industries, ensuring that products retain their integrity from production to delivery. These solutions encompass a range of facilities and equipment designed to keep goods at specific temperatures.
Among the diverse options available are walk-in refrigerators, chest freezers, blast chillers, and pharmaceutical-grade cold storage units. Each type suits different needs based on factors such as temperature range, capacity, accessibility, and energy efficiency. Moreover, technological advancements have introduced sophisticated features like real-time monitoring and automated temperature control, enhancing the reliability of these systems.
The importance of selecting the right cold storage solution cannot be overstated. Businesses need to consider:
- The nature of their products
- Storage life requirements
- The scale of storage needed
- Regulatory compliance concerns
These factors significantly influence the choice of cold storage, ensuring products are kept in prime condition while optimizing operational cost and efficiency. Hence, an understanding of the various types of cold storage and their ideal applications is crucial for making informed decisions that align with both product needs and business objectives. Through this article, insights into these types will be provided, serving as a guide to the maze of cold storage solutions.

Exploring the Different Types of Cold Storage
Cold storage is crucial for preserving perishable goods by maintaining specific temperatures to prolong their shelf life. Various types of cold storage units have been designed to meet the diverse needs of industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture.
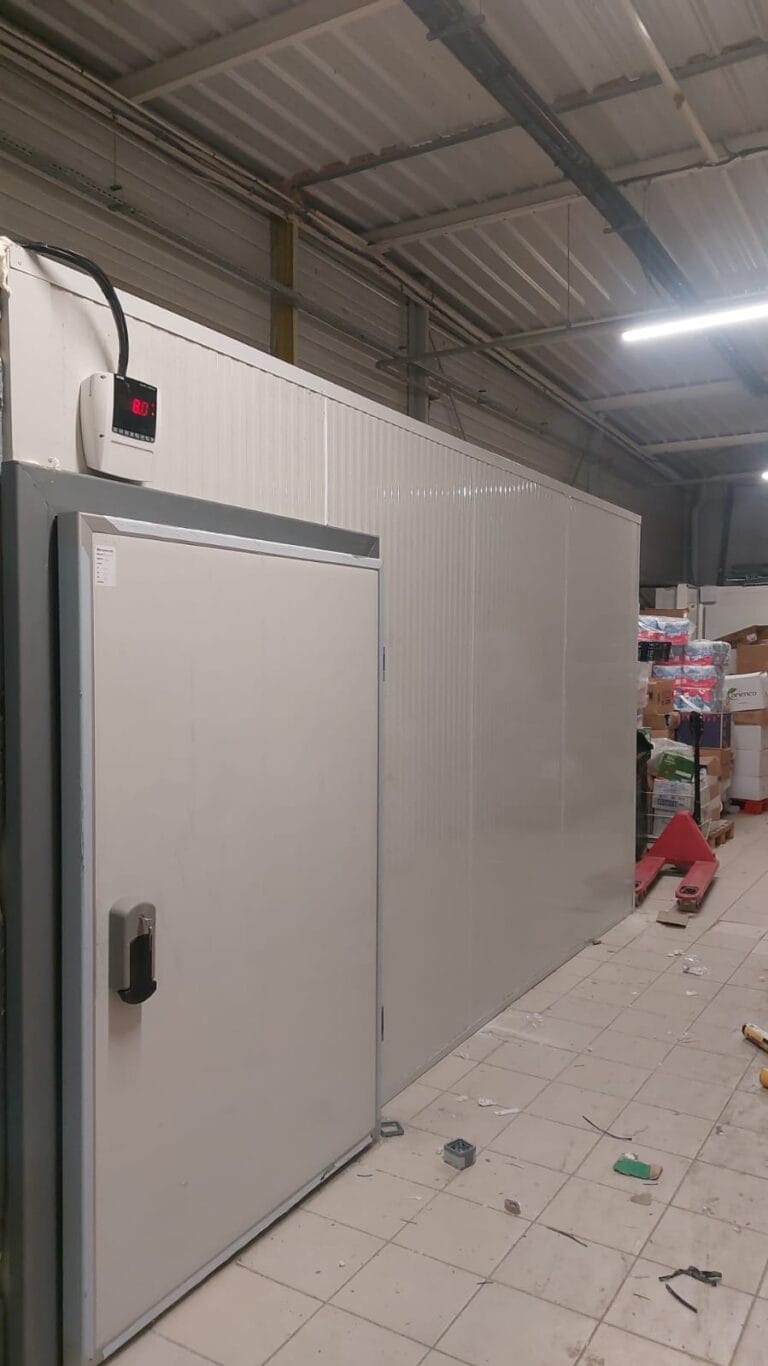
- Walk-In Refrigerators/Freezers: These are among the most common types of cold storage, capable of storing a wide range of goods. Walk-in units are ideal for businesses that need to store large quantities of perishable items and require regular access to them.
- Refrigerated Containers: Portable and versatile, refrigerated containers are used for both storage and transportation of goods. They are ideal for businesses that need a mobile solution or lack permanent facilities.
- Blast Freezers: These are essential for quickly reducing the temperature of products, especially food items, to prevent bacterial growth. Blast freezers are typically used in processing plants where rapid cooling is a critical part of the production process.
- Pharmaceutical-Grade Cold Storage: This type involves maintaining precise temperatures and often includes redundant systems to ensure constant cooling. Pharmaceutical-grade units are crucial for the safe storage of medicines and vaccines.
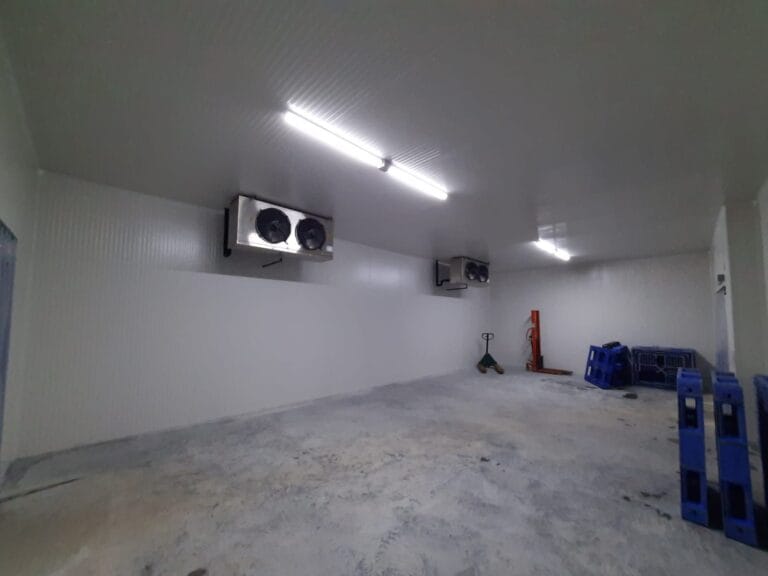
- Cold Rooms: Larger than walk-in units, cold rooms are designed for storing massive quantities of goods and are typically found in warehouses. They can be custom-built to specific sizes and temperatures as per requirement.
- Cryogenic Freezers: Employing extremely low temperatures, cryogenic freezers use liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide for cooling. These are perfect for preserving biological samples and for use in scientific research.
- Ultra-Low Temperature Freezers: These are specialized freezers that maintain temperatures between -40°C and -80°C. They’re critical in research and medical facilities where the preservation of samples at ultra-low temperatures is necessary.
Each cold storage type comes with distinctive features and costs, which must be considered alongside the storage needs. Choosing the right type ensures energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and most importantly, the integrity of the perishable goods stored within.

Refrigerated Warehouses: Features and Suitability
Refrigerated warehouses are essential components of the cold storage industry, accommodating a broad range of temperature-sensitive goods. These facilities feature robust refrigeration systems designed to maintain specific temperatures, often ranging from just above freezing to 4°C (39°F), which is ideal for prolonging the shelf life of perishable items.
Key Features:
- Temperature Control: The primary function is to keep perishable goods such as fruit, vegetables, dairy, and meat in a state of preservation by controlling the storage temperature.
- Humidity Regulation: To prevent dehydration and spoilage, refrigerated warehouses maintain optimal levels of humidity.
- Inventory Management Systems: Integration with advanced technology allows for real-time tracking, monitoring, and management of inventory.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern refrigerated warehouses incorporate energy-efficient systems to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Suitability:
Refrigerated warehouses are typically utilized by industries that require consistent temperature regulation for their products. They are most suitable for:
- Food and Beverage Industry: Ensures freshness and safety of perishable products like dairy, fresh produce, and ready-to-eat meals.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used for storing medication and vaccines that need to be kept cool to maintain efficacy.
- Horticulture: For flowers and plants, consistent temperatures can extend the viability and marketability of these products.
- Cosmetics: Certain beauty products have active ingredients that need refrigeration to avoid degradation.
Refrigerated warehouses are a pivotal link in the cold chain, enabling the transition of goods from the producer to the market while maintaining quality and safety standards. Their strategic location, often near transportation hubs, aid in minimizing the time perishables spend in transit, thereby reducing the risk of spoilage and ensuring the delivery of high-quality products to consumers.
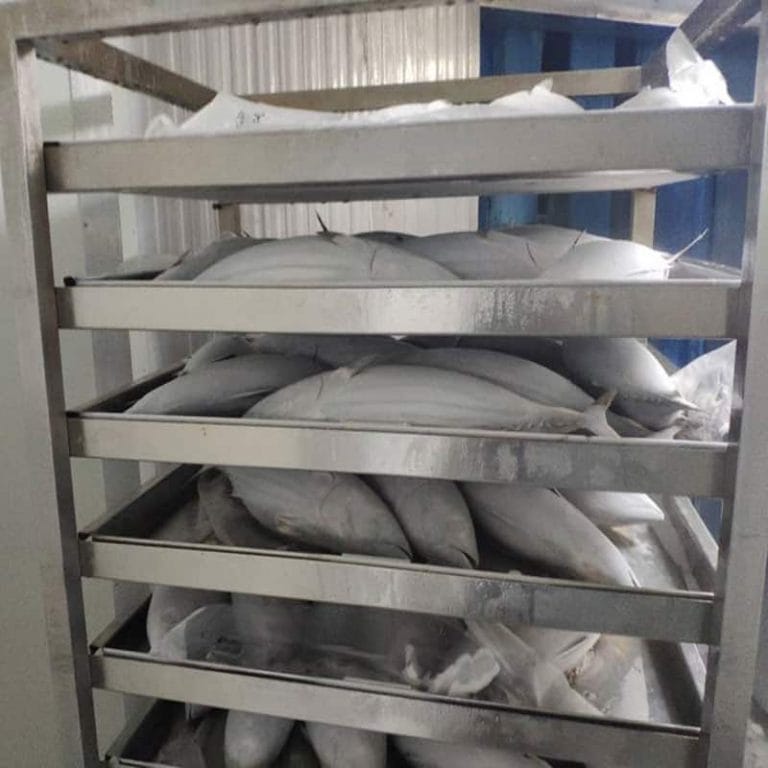
Blast Freezers and Their Role in Food Preservation
Blast freezers play a critical role in the food industry, specifically in the area of food preservation. By rapidly reducing the temperature of food products, they inhibit the growth of microorganisms that cause spoilage and decay. This swift freezing process is critical for maintaining the quality, texture, and nutritional value of the food.
The core function of a blast freezer is to bring down the temperature of foodstuffs so quickly that the ice crystals formed are very small. This is important because large ice crystals that can form during slower freezing processes damage the cellular structure of the food, leading to a decline in quality and consistency.
- Blast freezers are often used in the seafood and meat industries where freshness is paramount. Fish, for instance, must be frozen quickly to preserve its texture and taste.
- They are also essential for the ice cream industry, where achieving the correct type of crystallization is critical for texture.
- In the bakery sector, blast freezing allows for dough to be frozen without affecting yeast viability, ensuring the quality of baked goods even after thawing.
Blast freezing often serves as a preliminary step before storage in traditional freezers or before transportation. This initial rapid freezing phase makes subsequent cold storage more efficient, as products are already stabilized and less prone to temperature fluctuations which can affect quality.
The benefits extend beyond quality preservation. Blast freezing also enables food producers to safely and conveniently stockpile products, which can help in managing supply chains and reducing waste. Furthermore, it allows businesses to take advantage of seasonal produce by freezing excess stock for use throughout the year.
In short, blast freezers are an indispensable tool within the food industry, optimizing both the shelf life and quality of foodstuffs while supporting efficient and sustainable production practices.

Pharmaceutical Cold Storage: Maintaining Integrity of Medicines
The pharmaceutical industry is governed by stringent regulations to ensure the safety and efficacy of medicines. One critical aspect of pharmaceutical management is the proper storage of products, particularly those requiring strict temperature control to maintain their integrity. Here’s how cold storage plays a pivotal role:
- Controlled Environment: Most medicines must be stored at specific temperatures. A controlled environment eliminates the risk of temperature fluctuations that can degrade the product. Pharmaceutical cold storage provides a stable, controlled environment for vaccines, biologics, and other temperature-sensitive products.
- Advanced Monitoring Systems: These facilities often feature state-of-the-art monitoring systems. These systems provide real-time data and alerts to manage temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions, ensuring that any deviations are addressed promptly to safeguard the integrity of stored medicines.
- Compliance with Regulations: Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have strict guidelines for the storage of pharmaceuticals. Cold storage solutions must comply with these regulations, ensuring that products are stored within the required temperature ranges and that comprehensive records are kept for traceability and auditing purposes.
- Secure Access: Pharmaceutical cold storage facilities have strict security protocols to protect sensitive products from theft, tampering, or contamination. Access is typically restricted to authorized personnel only, with secure entry systems and surveillance in place.
- Cold Chain Logistics: The use of cold storage is critical in maintaining the cold chain during logistics. From the point of manufacture through to delivery, cold storage ensures that temperature-sensitive medicines remain within their required temperature range, thereby preserving their therapeutic properties.
By implementing these measures, pharmaceutical cold storage helps maintain the integrity and efficacy of medicines, which is crucial for patient safety and the overall trust in healthcare systems.
Cold Rooms vs Walk-in Freezers: Comparing the Essentials
When selecting cold storage solutions, it’s crucial to differentiate between cold rooms and walk-in freezers to match the right option with the intended application.
- Temperature Range: Cold rooms generally operate just above 0°C and are primarily used to prevent spoilage of perishable items such as produce or dairy. Walk-in freezers, on the other hand, sustain much lower temperatures, typically between -18°C to -22°C, creating an environment suitable for long-term preservation of items like meats and frozen foods.
- Insulation and Refrigeration: Both cold rooms and walk-in freezers require effective insulation to maintain constant temperatures. However, walk-in freezers necessitate higher-grade insulation and more powerful refrigeration systems due to their colder operational temperatures.
- Size and Customisation: Cold rooms can often be customized in size and shape to suit the needs of a business. Walk-in freezers are also adaptable but may have more stringent structural requirements due to the need for thicker insulation and more robust cooling equipment.
- Energy Consumption: Walk-in freezers usually consume more energy than cold rooms because of their lower temperature requirements. This aspect should be taken into account when considering the ongoing operational costs.
- Usage Applications: Cold rooms are ideal for supermarkets, catering businesses, and hospitals where frequent access to chilled, but not frozen, products is necessary. Walk-in freezers are more common in settings that require bulk storage of frozen products, such as food processing plants and large-scale catering facilities.
Selecting between a cold room and a walk-in freezer hinges on understanding these differences to ensure that the chosen cold storage solution optimally aligns with the specific needs of the business regarding product type, storage size, temperature requirements, energy efficiency, and budget considerations.
Ultra-Low Temperature Freezers for Sensitive Applications
Ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers are critical for storing biological samples such as viruses, bacteria, cells, and tissue, which require precise and consistent temperatures to remain viable. These freezers typically operate in a range between -40°C to -86°C. Laboratories, hospitals, and research facilities utilise ULT freezers for long-term preservation of critical biological samples where higher temperatures could trigger degradation.
- Biomedical Research: For the safe storage of biological specimens, ULT freezers are indispensable in biomedical research. They provide the stability needed for the accurate comparison of samples over extended periods.
- Pharmaceuticals: Many pharmaceutical products, especially biologic drugs and vaccines, require a stringent temperature controlled environment which ULT freezers can provide.
- Genetic Material: Genetic research labs entrust ULT freezers with the storage of DNA and RNA samples, where even minor temperature fluctuations can compromise sample integrity.
- Epidemiology: In the study of epidemics, it is crucial to maintain the viruses at stable low temperatures to prevent mutation or degradation for ongoing and future studies.
The design of ULT freezers maximizes storage capacity while minimizing the unit’s footprint. Some high-end models incorporate inventory management systems that allow for the tracking of stored items, which is particularly beneficial in high-throughput environments. Despite their low temperatures, modern ULT freezers are designed with energy efficiency in mind and often include features such as vacuum insulation panels and low-energy compressors.
A critical consideration for using ULT freezers is their maintenance requirements. Consistent temperature monitoring and calibration are mandatory to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, given the low temperatures, proper personal protective equipment, such as gloves and face shields, is essential to protect staff during the handling of items within ULT freezers. Regular defrosting and servicing are necessary to guarantee a long lifespan and reliability.
Transport Refrigeration Units: Cold Storage on the Move
Transport refrigeration units (TRUs) are critical in maintaining the cold chain during the transit of perishable goods. Designed to control the temperature of sensitive products, TRUs are used in a variety of vehicles, including trucks, shipping containers, and railroad cars.
- Trucks: TRUs outfitted on trucks provide flexibility for the distribution of goods across regional and national distances. They vary in size from small van-sized units for local deliveries to large trailers for cross-country hauls.
- Shipping Containers: Refrigerated containers, or reefers, are equipped with TRUs, allowing for perishable items to be transported across oceans without spoilage.
- Railroad Cars: Railcars with TRUs are an efficient means to move large quantities of temperature-sensitive goods over land, especially when time is not the primary concern.
Their versatility and reliability make TRUs ideal for a broad range of applications:
- Transporting pharmaceuticals that require strict temperature controls to remain effective.
- Delivery of fresh produce, dairy products, and other food items that need to be kept chilled or frozen to prevent spoilage and ensure food safety.
- Carrying floral shipments that demand specific temperature settings to preserve freshness and extend shelf life.
- Moving sensitive electronics or artwork that could be damaged by temperature fluctuations during transit.
Crucially, TRUs need constant power to maintain the desired temperature. This is typically provided by diesel generators for road and rail modes, while marine shipping containers can be plugged into the ship’s power supply. Recently, battery-powered and hybrid systems have also started to gain traction, leading to more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly alternatives.
Monitoring is another essential aspect, as it ensures the temperature remains within the pre-set range throughout transportation, enabling intervention if any deviations occur. This is achieved through sophisticated telemetry systems that provide real-time data to carriers and clients.
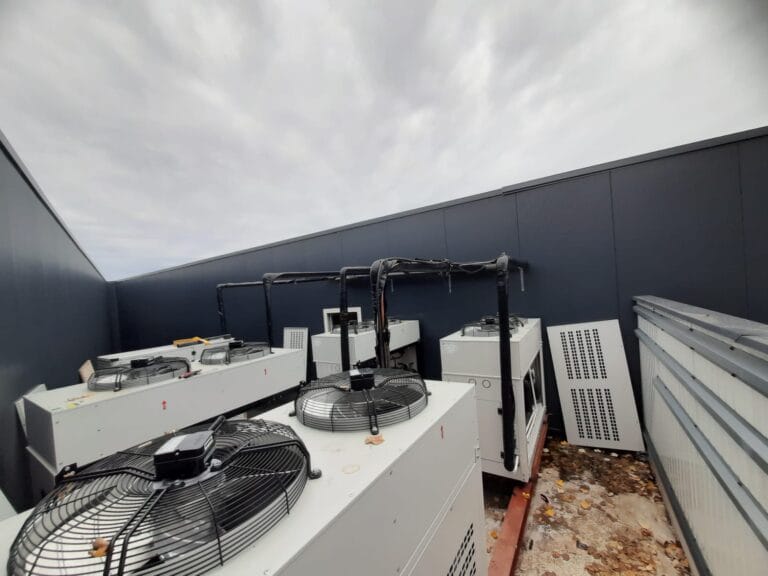
The Importance of Insulation and Energy Efficiency in Cold Storage
Optimal insulation is fundamental in the architecture of cold storage facilities. It serves as the quintessential barrier that mitigates thermal transfer between the interior of a refrigerated environment and the external temperatures. Proper insulation ensures that the cooling systems are not overtaxed, which can lead to increased energy consumption and higher operational costs.
Energy efficiency, too, is pivotal within cold storage operations. It is not solely about cost savings – although significant; it’s additionally about reducing the environmental impact inherent in energy-intensive storage solutions. Facilities that place a heavy emphasis on energy efficiency contribute to a lower carbon footprint through reduced energy use.
Improved insulation and energy-efficient technologies can lead to:
- Lower operational costs by reducing the amount of energy required to maintain desired temperatures.
- Increased longevity and reduced maintenance for cooling systems as they operate under less strain.
- Enhanced product integrity as stable temperatures reduce the risk of spoilage or quality degradation.
- Regulatory compliance, as many regions now enforce stringent guidelines on emissions and energy usage for industrial entities.
Implementing advanced materials such as vacuum-insulated panels, selecting appropriate refrigerants, and adopting smart technologies for monitoring and managing energy use are tactics used to optimize energy performance in cold storage. Furthermore, design considerations such as the thermal envelope, door seals, and even facility orientation play significant roles.
Ultimately, the marriage of insulation and energy efficiency is not merely beneficial but essential. Operators who invest in these features will not only see cost benefits but will also position themselves as responsible and sustainable participants in the cold supply chain.

Selecting the Right Cold Storage Type for Your Industry
Choosing the proper cold storage type is essential to ensure that goods are kept at optimal temperatures while maximizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Various factors must be considered when selecting the right cold storage solution for a specific industry:
- Capacity and Scalability: Determine the volume of products that require cooling or freezing and anticipate future growth. Businesses with fluctuating inventory levels may need modular cold storage that can be easily expanded or reduced.
- Specific Temperature Requirements: Different products require different temperature ranges. For example, the pharmaceutical industry may need ultra-low temperature freezers, while fruits and vegetables may be best stored in a chilled environment above zero degrees Celsius.
- Energy Efficiency: Operational costs can be significant, so opting for energy-efficient units with good insulation and modern cooling systems can reduce long-term expenses.
- Compliance and Standards: Ensure that the selected cold storage meets industry-specific regulations and guidelines to guarantee product safety and quality.
- Location and Accessibility: Logistics and transportation play a role; cold storage should be conveniently located to minimize transit times and costs while maintaining product integrity.
- Technology Integration: Advanced monitoring systems and technologies can help track inventory, maintain optimal conditions, and alert personnel to any temperature deviations.
Industries and Cold Storage Types:
- Food and Beverage: Walk-in refrigerators/freezers, blast chillers, and cold rooms tailored for produce, dairy, meats, and frozen goods.
- Pharmaceuticals: Ultra-low temperature freezers, cryogenic storage, and secure climate-controlled facilities for sensitive medications and vaccines.
- Agriculture: Bulk storage coolers and processing area chillers for fresh produce.
- Floral: Refrigerated display cases and storage coolers with humidity control to prolong the freshness of flowers.
- Chemicals: Hazardous material storage with temperature regulation to prevent decomposition or reactions.
- Data Centres: Contained cold aisles and precision air conditioners for server cooling to ensure optimal performance.
By carefully assessing these considerations, industries can identify the most appropriate cold storage solutions that align with their specific needs, thus guaranteeing the safety, quality, and longevity of their temperature-sensitive products.
Best Practices in Managing and Operating Cold Storage Facilities
Managing and operating cold storage facilities requires meticulous attention to detail, adherence to safety protocols, and a commitment to efficiency. Here are some best practices:
- Maintain Strict Temperature Control:
- Constantly monitor temperature levels using automated systems to ensure they remain within optimal ranges.
- Schedule regular maintenance to check the insulation and refrigeration units to prevent temperature fluctuations.
- Ensure Proper Inventory Management:
- Implement a first-expiry-first-out (FEFO) system to reduce the risk of spoilage.
- Use inventory management software for real-time tracking and ensure stock rotation is consistent with product shelf life.
- Focus on Energy Efficiency:
- Invest in modern, energy-efficient refrigeration systems and LED lighting to reduce the facility’s carbon footprint.
- Conduct energy audits to identify areas for improvement and implement insulation upgrades where necessary.
- Implement Safety Measures:
- Provide personal protective equipment (PPE) to all personnel to ensure safety at sub-zero temperatures.
- Establish emergency protocols and regularly train staff on how to act during system failures or power outages.
- Regular Cleaning and Sanitation:
- Schedule regular cleaning to prevent contamination and ensure compliance with health regulations.
- Sanitize storage areas to remove any bacteria or pests that could harm the stored goods.
These practices are essential in keeping cold storage operations effective, safe, and in compliance with industry standards. By prioritising these elements, managers can ensure the longevity and profitability of their cold storage facilities.
Understanding Cold Chain Logistics and Integration
Cold chain logistics is the process of managing the transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive goods in a way that ensures their quality and safety from origin to destination. This process is vital in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, and beverages, where products are prone to spoilage if not kept at the required temperatures.
Integration in cold chain logistics means the seamless operation of the various components involved, including:
- Cold Storage Facilities: Central to cold chain logistics, these are equipped to store goods at specific temperatures. Facilities range from refrigerated warehouses to cryogenic storage units, depending on the product requirements.
- Refrigerated Transport: Vehicles include refrigerated trucks, sea containers, and air cargo, which are used to move products between production sites, storage facilities, and to the final consumer.
- Monitoring Systems: Real-time temperature monitoring and tracking systems ensure that the products are constantly maintained at the ideal temperature throughout the supply chain.
- Packaging: Insulated and thermal packaging materials are crucial to maintain product temperatures. This includes containers, wraps, and gel packs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Cold chain logistics must adhere to strict regulations, which vary between countries and products. Proper integration ensures compliance at every step.
- Information Systems: To efficiently manage the cold chain, robust IT systems are necessary to integrate all the logistic components, providing a central point for data collection and analysis.
Effective integration in cold chain logistics not only preserves the quality of sensitive products but also increases efficiency, reduces waste, and enhances product safety. For businesses that rely on cold storage, understanding and implementing an integrated logistics solution are vital for sustaining a competitive edge in the market.

The Future of Cold Storage: Innovations and Trends
The future of cold storage is teeming with technological advancements aimed at enhancing efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and increasing the reliability of temperature-controlled environments. Here are some of the latest innovations and trends shaping the future of cold storage:
- Advancements in Insulation Materials: The use of new insulation technologies, such as vacuum insulated panels (VIPs) and phase change materials (PCMs), is on the rise. These materials offer superior thermal resistance and minimise energy loss, significantly improving the sustainability of cold storage facilities.
- Integration of IoT and AI: The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionising cold storage operations. Sensors and smart systems are providing real-time monitoring and analytics, leading to predictive maintenance and optimised inventory management.
- Automation and Robotics: Robotics and automation are becoming increasingly prevalent in cold storage logistics. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and robotic picking systems streamline the handling process, lower the risk of human error, and improve safety for workers in cold environments.
- Energy-Efficient Refrigeration Systems: Innovative refrigeration systems are being developed to reduce energy usage and environmental impact. Technologies like CO2 refrigeration systems and magnetic cooling offer eco-friendly alternatives to traditional refrigerants.
- Building Design and Modular Facilities: The design of cold storage buildings is evolving to include features such as dynamic airflow systems and retractable insulating walls. Modular and mobile cold storage units are also gaining traction, providing flexibility to respond to changing market demands.
These emerging technologies demonstrate the industry’s commitment to improving operational efficiency, maintaining product integrity, and striving for sustainability in cold storage solutions. As the demand for perishable goods continues to grow, so too will the innovation in the cold storage sector, ensuring the industry is well-equipped to meet future challenges.
Conclusion: Matching Applications with the Ideal Cold Storage Solutions
In the realm of perishable goods management, selecting the appropriate cold storage solution is paramount for maintaining product integrity, optimizing shelf life, and ensuring safety. It’s critical to weigh the specific requirements of the products against the features of each cold storage option.
- Pharmaceuticals and medical supplies often necessitate ultra-low temperature freezers to preserve the efficacy of drugs and biological materials. These settings are sensitive, where precise temperature control is essential, and thus require specialized equipment.
- Food and beverage industries, on the other hand, may find that refrigerated warehouses provide the ideal environment for their inventory. They can benefit from larger, scalable spaces that maintain a constant, but not necessarily extremely low, temperature.
- For agricultural products, which may only need short-term storage before distribution, walk-in coolers or cold rooms could provide a cost-effective and adequately controlled environment.
- The technology sector, especially for companies that require cold storage of sensitive electronics or data servers, will look towards sophisticated climate-controlled solutions that can prevent overheating and ensure the longevity of their equipment.
- Retail and food service businesses, including restaurants and supermarkets, typically require a combination of reach-in refrigerators or display coolers for daily operations, providing easy access and appropriate storage for consumer products.
To conclude, the careful pairing of cold storage solutions to their applications is not a one-size-fits-all scenario. Varied industries have distinct needs that dictate the cold storage type — from modular units to expansive warehouses. By understanding these unique requirements and how they translate into cold storage demands, businesses can ensure they invest in the most efficient, cost-effective, and suitable systems available, thereby securing their products’ quality and extending their usability.