Introduction to Walk-in Cold Rooms
Walk-in cold rooms are essential storage solutions for industries requiring temperature-controlled environments. Commonly used in catering, food production, pharmaceuticals, and floral industries, these rooms maintain low temperatures to preserve perishable items. Understanding the basic components and functionalities of these units can aid in comparing prices and features effectively.
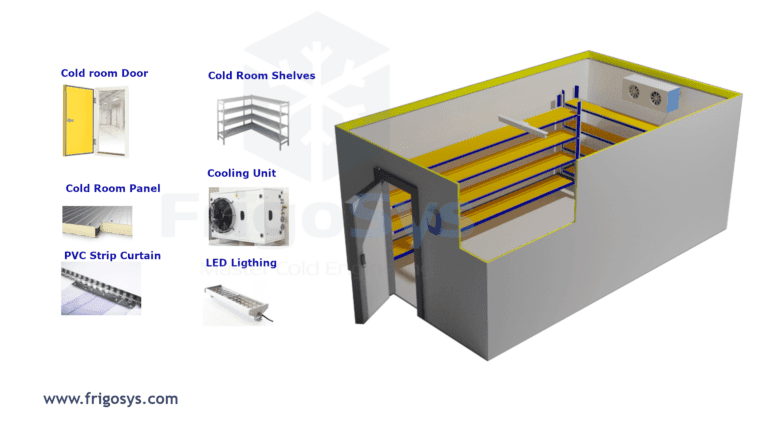
Key Components
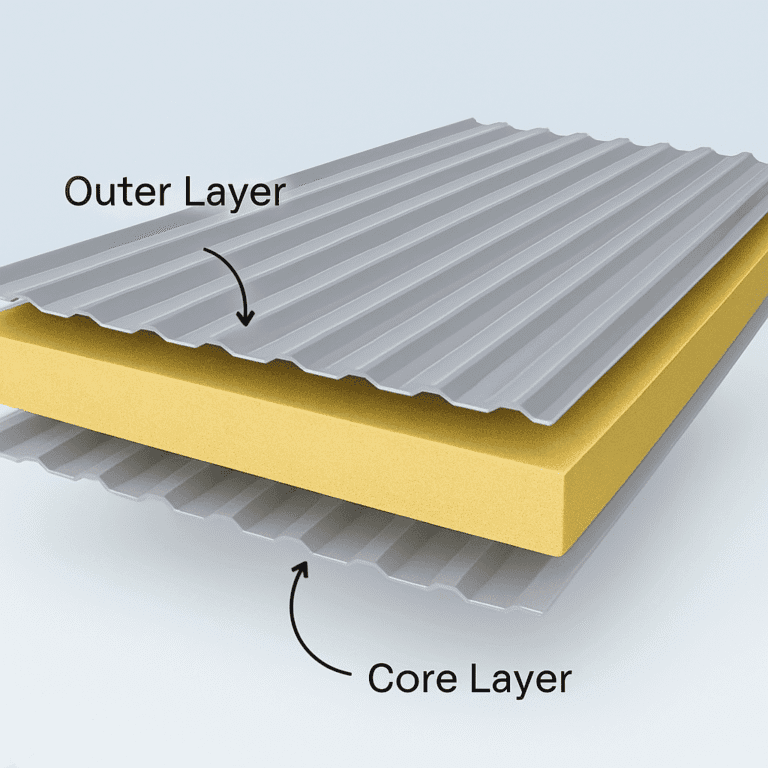
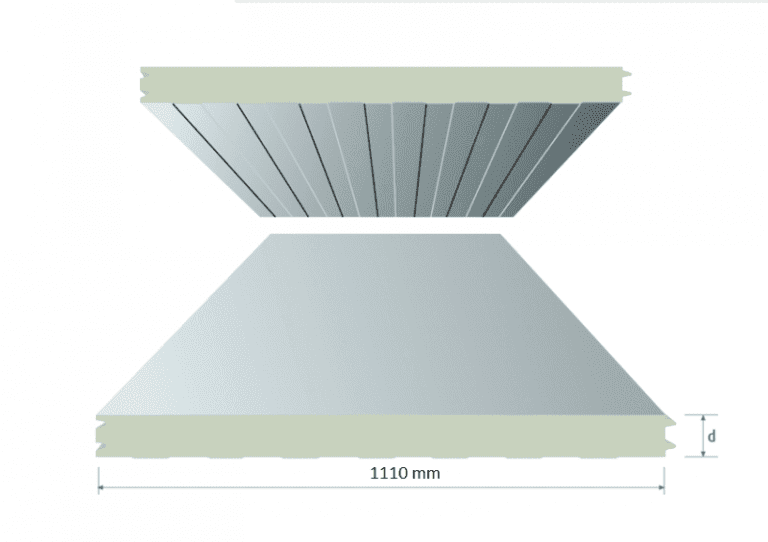
- Insulated Panels: Made from polyurethane or polystyrene, these panels provide the necessary insulation.
- Refrigeration System: This encompasses the compressor, evaporator, and condenser to regulate temperature.
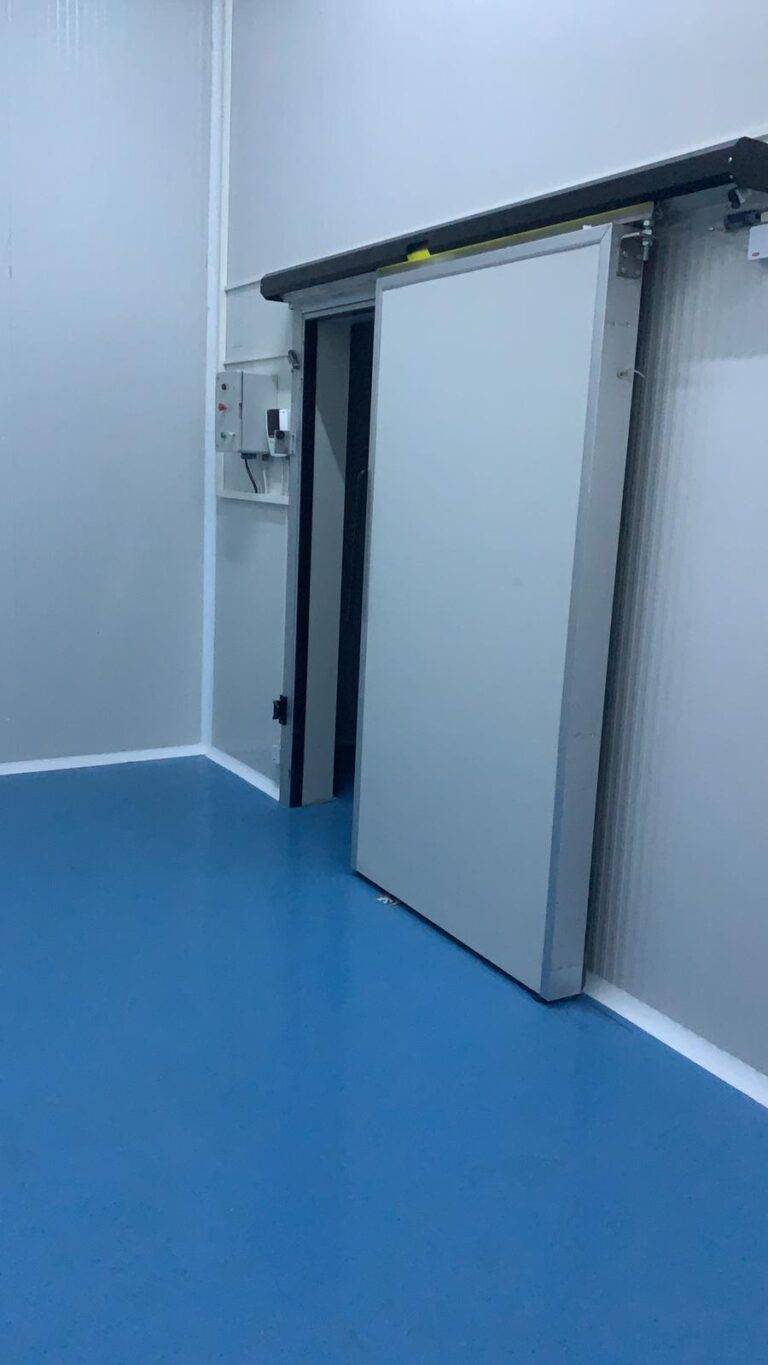
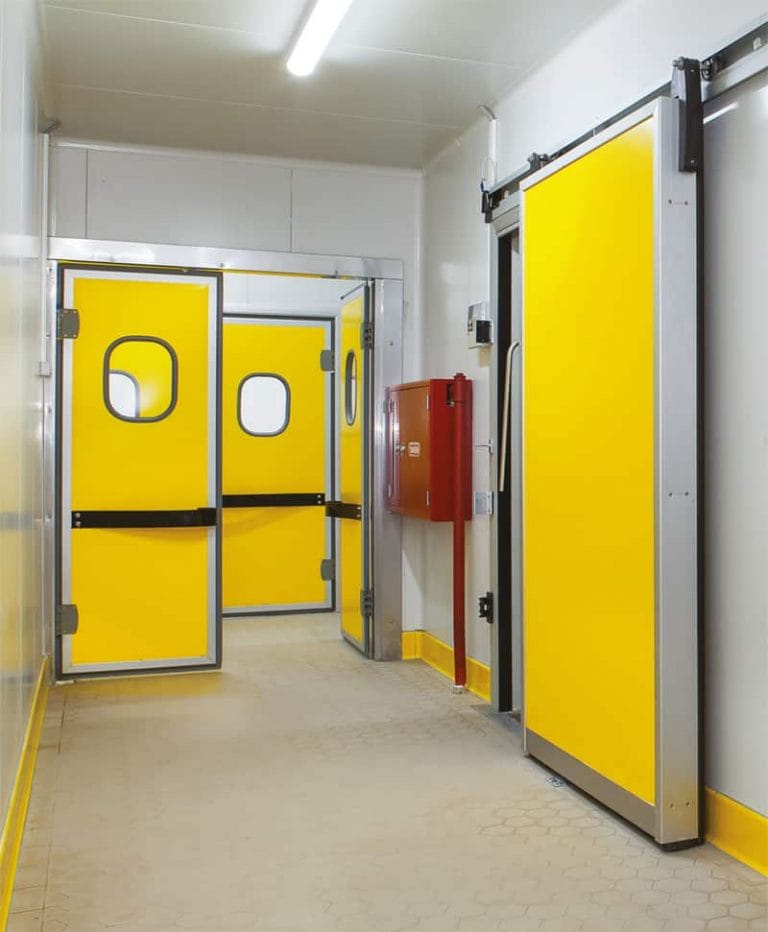
- Walk-in Cold Room Doors: Typically heavy-duty with insulation and tight seals to maintain internal temperatures.
- Flooring: Non-slip, durable materials to withstand low temperatures and heavy traffic.
- Control Systems: Electronic panels to monitor and adjust temperature and humidity levels.
Common Features
- Temperature Range: Most can maintain temperatures between -40°C to +8°C.
- Customization: Various sizes and configurations to fit specific needs.
- Shelving: Adjustable racks and shelves for organized storage.
- Lighting: Built-in lighting systems that are energy efficient and suitable for low temperatures.
- Alarms: Temperature and door alarms to ensure compliance with storage standards.
Applications
Walk-in cold rooms are utilized across various sectors:
- Restaurants and Catering: Storage of fresh produce, meat, and dairy products.
- Pharmaceuticals: Preservation of temperature-sensitive drugs and vaccines.
- Floral Industry: Keeping flowers fresh by maintaining optimal humidity and temperature.

Considerations
When comparing walk-in cold rooms, factors such as size, temperature range, energy efficiency, and specific features must be evaluated. The needs of the industry and regulatory requirements may also influence the choice of features and specifications.
Understanding these essential aspects will provide a solid foundation for comparing different walk-in cold room options.
Enhanced Storage Capacity
When comparing walk-in cold rooms’ prices and features, enhanced storage capacity is a critical aspect to consider. It directly impacts the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the cold room. Key factors influencing storage capacity include:
1. Customizable Shelving Systems
- Adjustable Shelves: Flexible shelving options enhance versatility, allowing businesses to reorganize as inventory needs change.
- Heavy-Duty Racks: Strong, durable racks can support a higher volume of goods, preventing damage and maximizing space.
- Specialized Racks: Designed for specific products, such as meat or dairy, these racks can help reduce spoilage and improve workflow.
2. Optimal Space Utilization
- Vertical Storage: Utilizing vertical space effectively can significantly increase the total storage capacity without expanding the room’s footprint.
- Compact Design: Innovative designs that minimize wasted space can offer more storage in a smaller area, reducing energy and real estate costs.
- Modular Layouts: These allow for easy expansion as storage needs grow, providing flexibility for future business scaling.
3. Efficient Organization
- Categorization: Proper organization helps in quickly locating items, reducing time spent with open doors and maintaining consistent internal temperatures.
- Labeling Systems: Clear labeling and inventory management systems assist in tracking stock levels, expiration dates, and restocking needs.
- Automated Inventory Systems: Advanced technology for automatic tracking can further streamline operations, ensuring an efficient use of storage space.
4. Structural Considerations
- Insulation Quality: High-quality insulation helps maintain cold temperatures efficiently, protecting stored goods and reducing energy consumption.
- Door Design: Self-closing doors with airtight seals ensure minimal temperature variation and optimum energy use.
- Flooring Systems: Durable, easy-to-clean floors contribute to efficient maintenance and safe storage practices.
5. Planning and Design
- Needs Assessment: Thorough analysis of storage requirements—considering both current and future needs—ensures appropriate capacity selection.
- Budget Allocation: Balancing the initial investment with long-term savings from efficient storage can optimize budgetary decisions.
- Industry Standards Compliance: Ensuring the design meets all regulatory requirements guarantees safety and longevity.
Understanding these components will assist in selecting a walk-in cold room that not only fits the budget but also offers the best storage solutions tailored to specific business needs. Enhanced storage capacity ensures efficient operations, cost savings, and optimal product preservation.
Improved Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a critical factor when evaluating walk-in cold rooms. Units with better energy efficiency can significantly reduce operational costs. Several elements contribute to the energy efficiency of a walk-in cold room. These elements not only reduce energy consumption but also enhance overall cost-effectiveness.
Insulation
- Quality Materials: High-quality insulation materials, such as high-density polyurethane foam, improve thermal resistance.
- Thickness: Thicker insulation provides better temperature control by minimizing heat exchange.
- Sealing: Properly sealed doors and panels prevent air leakage, ensuring the internal temperature remains constant.
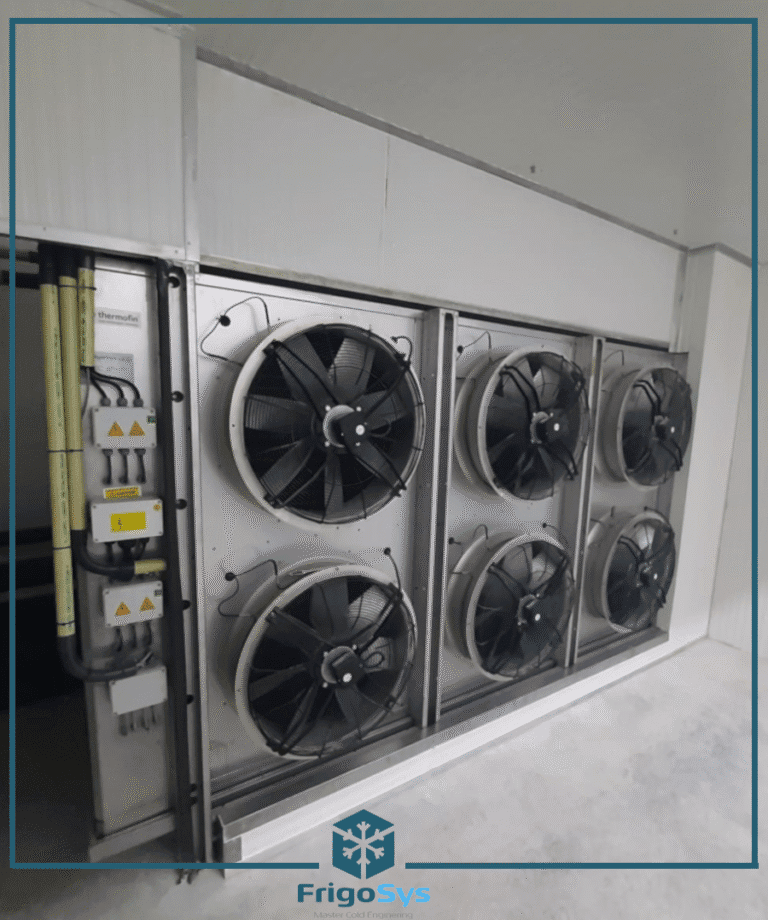
Refrigeration System
- Compressor Efficiency: Modern, high-efficiency compressors consume less power, thus lowering electricity bills.
- Variable Speed Compressors: These adapt to cooling demands, providing energy savings by reducing compressor workload when full power is not necessary.
- Advanced Controls: Digital controllers and automated systems optimize compressor operation and defrost cycles, enhancing overall efficiency.

walk in cold room cooling unit
Ventilation
- Efficient Air Circulation: Properly designed ventilation systems ensure even distribution of cold air, reducing energy wasted on overcooling specific areas.
- Heat Recovery Systems: These systems capture and reuse heat expelled from compressors to preheat incoming air, reducing the demand on cooling units.
Lighting
- LED Lighting: LEDs are more energy-efficient and generate less heat than traditional lighting options, thus reducing cooling load.
- Motion Sensors: Automated lighting that activates only when necessary saves additional energy.
Doors
- Self-Closing Mechanisms: Doors that close automatically prevent unnecessary air exchange, maintaining internal temperature more effectively.
- Triple-Pane Glass: For rooms requiring visibility, triple-pane glass provides better insulation than single or double-pane options.

Design Considerations
- Door Seals and Gaskets
- High-quality door seals prevent cold air leakage and reduce temperature variations.
- Magnetic gaskets ensure tight closure, enhancing insulation efficiency.
- Optimal Airflow
- Proper airflow design avoids hot spots or areas with uneven temperature distribution.
- Fans and air curtains can enhance air circulation, maintaining consistent conditions.
Enhanced Food Safety and Compliance
When comparing walk-in cold room prices and features, it is essential to consider the implications for food safety and compliance with regulatory standards. A robust walk-in cold room can significantly improve food safety measures, ensuring that perishable goods remain fresh, reducing the risk of contamination, and maintaining compliance with industry regulations.
Important Safety Features
- Temperature Control: Precise temperature controls are crucial to maintain the ideal environment for various food products. This ensures that the internal temperature remains consistent and diminishes the chances of spoilage or bacterial growth.
- Shelving and Storage Solutions: Proper shelving and storage solutions enable systematic organization and minimize cross-contamination. Customizable shelving options are often available to suit different types of products and storage requirements.
- Alarm Systems: Alarm systems that alert staff to temperature fluctuations or door ajar situations enhance food safety. These alarms can be connected to mobile devices for real-time notifications, allowing for prompt corrective action.
Compliance Considerations
Regulatory compliance is non-negotiable in food storage and handling environments. Key compliance features include:
- Temperature Monitoring and Recording: Compliance with health regulations often requires continuous temperature monitoring and recording. Automated systems can log temperature data and generate reports that are essential during audits.
- Sanitation and Hygiene: The materials used in the construction of walk-in cold rooms should be easy to clean and resistant to mold and bacteria. Stainless steel and other non-porous materials are generally preferred.
- Energy Efficiency: Walk-in cold rooms with energy-efficient components not only reduce operational costs but also comply with environmental regulations. Features like LED lighting and high-efficiency compressors contribute to this.
Extended Shelf Life of Products
When comparing walk-in cold rooms prices and features, one significant benefit is the extended shelf life of products. By maintaining a controlled environment, walk-in cold rooms help preserve the quality and safety of various perishable items. Key factors influencing shelf life include consistent temperature, humidity control, and proper ventilation.
Temperature Control
- Consistency: Walk-in cold rooms offer consistent temperature levels, which is crucial for preventing spoilage.
- Customization: Many units provide customizable temperature settings tailored to specific products.
- Efficiency: Energy-efficient models contribute to maintaining low operational costs while delivering reliable performance.
Humidity Control
- Balanced Humidity: Proper humidity levels prevent dehydration or excessive moisture, which can affect product quality.
- Integrated Systems: Advanced cold rooms may come with built-in humidity control systems.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring and adjustments help maintain optimal conditions.

Ventilation
- Air Circulation: Good ventilation systems ensure uniform air distribution, mitigating hot spots.
- Freshness: Adequate airflow helps retain product freshness by limiting mold growth.
- Odor Control: Effective ventilation reduces unwanted odors, enhancing the storage environment.
Impact on Various Products
- Meat and Seafood: Maintains freshness and inhibits bacterial growth.
- Dairy Products: Extends shelf life by preventing spoilage due to temperature fluctuations.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Preserve nutritional value and visual appeal.
- Pharmaceuticals: Ensures efficacy by storing at recommended temperatures.
Additional Features
- Remote Monitoring: Modern cold rooms often feature remote monitoring capabilities, allowing operators to keep track of conditions from a distance.
- Alarms and Alerts: Built-in systems can notify users of any deviations from set parameters, ensuring prompt corrective action.
- Energy Savings: Energy-efficient designs not only cut costs but also contribute to environmental sustainability.
By optimizing these elements, walk-in cold rooms help businesses reduce waste and improve product management, ultimately leading to cost savings and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Operational efficiency in a walk-in cold room is pivotal for businesses in the food and beverage industry, pharmaceuticals, and other sectors requiring cold storage. Efficient operations not only reduce energy consumption but also improve the lifespan of the cold room and its components.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation
Higher Insulation Standards:
- Cold rooms with superior insulation materials such as polyurethane foam (PUF) and extruded polystyrene (XPS) help maintain consistent internal temperatures.
- Better insulation reduces the frequency and duration of refrigeration cycles, which leads to lower electricity bills.
Energy-Efficient Refrigeration Units:
- Modern refrigeration units often come with high-efficiency compressors and fans.
- Some units offer variable speed options, allowing the refrigeration system to adjust its output based on real-time demands, further conserving energy.
Temperature Control and Monitoring
Advanced Temperature Control Systems:
- Digital thermostats provide precise temperature control, reducing the risk of spoilage.
- Remote monitoring systems enable real-time tracking and alert for any deviations, allowing for swift corrective action.

Automated Data Logging:
- Automated data logging systems can compile historical temperature data, enhancing traceability.
- These systems help ensure compliance with health and safety regulations, which is crucial for industries like pharmaceuticals and food services.
Design and Accessibility
Efficient Layouts:
- Walk-in cold rooms designed with efficient shelving and storage options maximize usable space.
- Adequate spacing ensures proper air circulation, maintaining uniform temperatures throughout the room.
Easy Access and Mobility:
- Features like automatic doors and anti-slip flooring contribute to safer and more efficient operations.
- Mobile shelving units help staff access products without disrupting the cold room’s internal temperature.
Routine Maintenance and Durability
Durability and Easy Maintenance:
- High-quality materials reduce wear and tear, minimizing maintenance needs.
- Modular designs allow easier replacement of parts, ensuring prolonged operational uptime.
Maintenance Alerts:
- Some advanced systems offer predictive maintenance alerts, helping operators schedule repairs before breakdowns occur.
By thoroughly considering these elements, businesses can choose a walk-in cold room that significantly enhances operational efficiency, ensuring a profitable and sustainable operation.
Cost Savings in the Long Run
When comparing walk-in cold room prices and features, it is crucial to consider potential cost savings over time. Initial purchase prices often dominate decision-making, but other factors contribute significantly to long-term savings. Below are key elements to consider:
Energy Efficiency
- Insulation Quality: Superior insulation reduces the energy required to maintain low temperatures. Thicker walls and high-quality materials can enhance thermal efficiency.
- Efficient Compressors: Modern compressors with variable speed options adjust power usage according to demand, reducing energy consumption.
- LED Lighting: Using LED lights, which emit less heat and are more energy-efficient, can lower operational costs.
Maintenance Costs
- Durable Materials: Cold rooms constructed with robust, corrosion-resistant materials generally require fewer repairs and replacements.
- Warranty and Service Plans: Opting for units with comprehensive warranties and service contracts can mitigate unexpected maintenance expenses.
- Modular Design: Modular cold rooms allow for easier replacement of faulty components, decreasing repair time and costs.
Inventory Management
Properly functioning walk-in cold rooms mitigate the risk of food spoilage, lowering inventory loss. Key features contributing to better inventory management include:
- Consistent Temperature Control: Advanced cooling systems ensure stable temperatures, preserving product quality.
- Remote Monitoring: Systems with remote monitoring capabilities can alert users to temperature fluctuations, allowing prompt corrective actions.
Return on Investment
Long-term cost savings can lead to a better return on investment (ROI). Factors influencing ROI include:
- Energy Rebates and Incentives: Energy-efficient units may qualify for rebates and incentives from utility companies or government programs.
- Reduced Utility Bills: Lower ongoing energy costs contribute to significant savings over the lifespan of the cold room.
Future-proofing
Investing in a high-quality walk-in cold room can provide cost advantages by:
- Scalability: Modular units can be easily expanded to meet growing business requirements, avoiding the need for new, costly installations.
- Technological Upgrades: Units with upgradable components ensure compatibility with future technological advancements, extending the useful life of the cold room.
Considering these factors when comparing walk-in cold room prices and features can result in more informed purchasing decisions, ultimately leading to substantial cost savings in the long run.
Scalability Considerations
- Modular Design:
- Modular cold rooms enable easy expansion by adding additional panels and sections as needed.
- This flexibility allows businesses to scale operations without significant downtime or disruption.
- Load Capacity:
- It’s crucial to consider the weight and volume of products the cold room will store.
- Scalable load capacity helps in adapting to growing inventory needs.
- Refrigeration Systems:
- Scalable refrigeration units can be upgraded or expanded to handle increased cooling demands.
- Energy-efficient options keep operational costs manageable during expansion.
- Technology Integration:
- Advanced monitoring systems and automation features can be integrated to enhance scalability.
- Remote temperature controls and alerts support efficient management of larger setups.
- Future-Proof Design:
- Planning for future scalability can save time and money.
- Selecting designs that accommodate potential growth ensures the cold room remains viable long-term.
In conclusion, focusing on customization and scalability ensures that a walk-in cold room meets both current needs and future demands, providing a tailored solution that supports business growth and operational efficiency.
Investment and Return on Investment (ROI)
When evaluating walk-in cold rooms, one must consider both the initial investment and the potential return on investment (ROI). The initial cost can vary significantly based on a range of factors, including size, materials, and additional features.
Initial Investment
The initial investment in a walk-in cold room includes several key components:
- Size and Capacity:
- Larger cold rooms tend to be more expensive.
- Determine the required storage capacity before deciding.
- Material and Construction:
- High-quality materials ensure better insulation and energy efficiency.
- Stainless steel interiors, while costlier, provide superior durability.
- Cooling System:
- The type of cooling system impacts both initial cost and long-term savings.
- Advanced systems with digital controls may require a higher initial investment but offer better energy management.
- Installation Costs:
- Professional installation is recommended for optimal performance.
- Consider any additional costs for site preparation or modifications.
- Accessories and Features:
- Shelving, lighting, and monitoring systems can add to the initial cost.
- Features such as remote monitoring enhance functionality but increase investment.
Ongoing Costs and ROI
Understanding ongoing costs is crucial for calculating ROI:
- Energy Efficiency:
- Efficient insulation and high-performance compressors reduce energy consumption.
- Energy-efficient models might have a higher upfront cost but lead to significant utility savings.
- Maintenance:
- Regular maintenance ensures longer lifespan and consistent performance.
- Include the cost of maintenance agreements and service contracts in the ROI calculation.
- Repairs and Replacements:
- High-quality cold rooms may have fewer repair requirements.
- Consider depreciation and potential future replacement costs.
- Operational Costs:
- Efficient operation minimizes downtime and spoilage, enhancing overall profitability.
- Advanced control systems can optimize temperatures and reduce waste.
Calculating ROI
To assess the ROI for a walk-in cold room, consider the following:
- Initial Costs: Summarize the total initial investment including purchase, installation, and additional features.
- Annual Savings: Estimate savings from reduced energy costs and decreased waste.
- Lifespan: Project the expected useful life of the cold room.
- Payback Period: Calculate the time required to recover the initial investment.
By leveraging these insights when comparing walk-in cold room options, businesses can make informed decisions that ensure both optimal performance and a favorable return on investment.
Practical Use Cases and Industries
Walk-in cold rooms serve a diverse array of industries, each with unique needs and applications. These specialized refrigeration units are critical in various sectors:
Food and Beverage
- Restaurants and Cafés: Essential for storing perishable ingredients and prepared dishes.
- Grocery Stores and Supermarkets: Ideal for preserving fresh produce, dairy products, and frozen goods.
- Food Processing Facilities: Required for chilling raw materials and finished products to ensure food safety and quality.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
- Hospitals and Clinics: Used for storing vaccines, blood products, and other temperature-sensitive medical supplies.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Necessary for maintaining the stability of drugs and medicinal ingredients.
- Laboratories: Vital for preserving biological samples and reagents critical to research.
Agriculture
- Dairy Farms: Important for storing milk and dairy products before transport.
- Fruit and Vegetable Farms: Essential for post-harvest cooling to prolong freshness and reduce waste.
- Meat and Poultry Producers: Crucial for chilling carcasses and meat products to prevent spoilage.
Floral and Horticulture
- Florists: Required to keep cut flowers fresh and vibrant.
- Plant Nurseries: Useful for storing bulbs, seeds, and delicate plants at optimal temperatures.
- Flower Wholesalers: Important for maintaining flower quality during distribution.
Hospitality and Catering
- Hotels and Resorts: Needed for large-scale food storage to meet guest demands.
- Event Catering: Essential for maintaining food safety for off-site events.
- Cruise Ships: Necessary for extended voyages to keep food supplies fresh.
Biotechnology and Research
- Biotech Companies: Use walk-in cold rooms to store sensitive biochemical substances.
- Research Institutions: Essential for maintaining controlled environments for experiments.
Brewing and Winemaking
- Microbreweries and Distilleries: Crucial for fermentation and aging processes.
- Wineries: Required for preserving grapes and wine at precise temperatures to ensure quality.
These varied applications highlight the versatility and importance of walk-in cold rooms across different sectors. Each industry has specific requirements, that influence the design, features, and cost of the cold rooms they need.
Conclusion: Making the Smart Investment
When considering walk-in cold rooms prices and features, it is crucial to look at multiple aspects to make an informed decision. Comparing prices alone is not enough, as various features, installation costs, and operational efficiencies can significantly impact long-term value.
Key Considerations
- Initial Costs
- Purchase Price: Evaluate the upfront cost while considering the brand and model.
- Installation Costs: Factor in delivery and setup expenses.
- Energy Efficiency
- Insulation Quality: Superior insulation can drastically cut energy consumption.
- Refrigeration System: Modern, energy-efficient systems can lower utility bills.
- Size and Capacity
- Internal Space: Assess the storage volume to ensure it meets business needs.
- Expandable Options: Consider models that allow future expansion.
- Temperature Control and Monitoring
- Precision: High-quality systems provide accurate temperature control.
- Alarm Systems: Critical alerts for temperature deviations ensure product safety.
- Durability and Materials
- Build Quality: Strong, corrosion-resistant materials prolong the unit’s life.
- Maintenance Needs: Opt for low-maintenance designs to reduce operational downtime.
- Compliance and Safety
- Regulations: Ensure the cold room meets local and federal regulations.
- Safety Features: Look for features like anti-slip flooring and emergency alarms.
- Vendor Support
- Warranty: A robust warranty can save considerable costs in repairs.
- Customer Service: Reliable support ensures timely help and maintenance.
Tips for Decision Making
- Compare Multiple Quotes: Gather and compare quotes from different suppliers.
- Read Reviews: Customer reviews provide insights into real-world performance.
- Ask for Demos: Whenever possible, ask for a demonstration to see the cold room in action.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate all costs involved over the lifespan of the cold room.
Final Thoughts
Investing in a walk-in cold rooms requires a comprehensive approach. Balancing price with essential features ensures a smart investment that meets operational needs while providing long-term value.